

In recent years, there have been many rapid charging claims that have been advertised. There are a handful of products, when compared to conventional charging, which can claim a small decrease in charge time. Our technique far surpasses any of these products and our charge algorithm is not commercially available on the market today.
High pulse current charging causes electrolyte stratification and unequal ion concentration at the electrodes. By reducing heat generating charge acceptance problems and electrochemical polarization, we are able to charge at exceptionally high currents. This drastically decreases the charge time. Our algorithm provides a pathway for the ions to disperse and the electrolyte to achieve a uniform distribution.
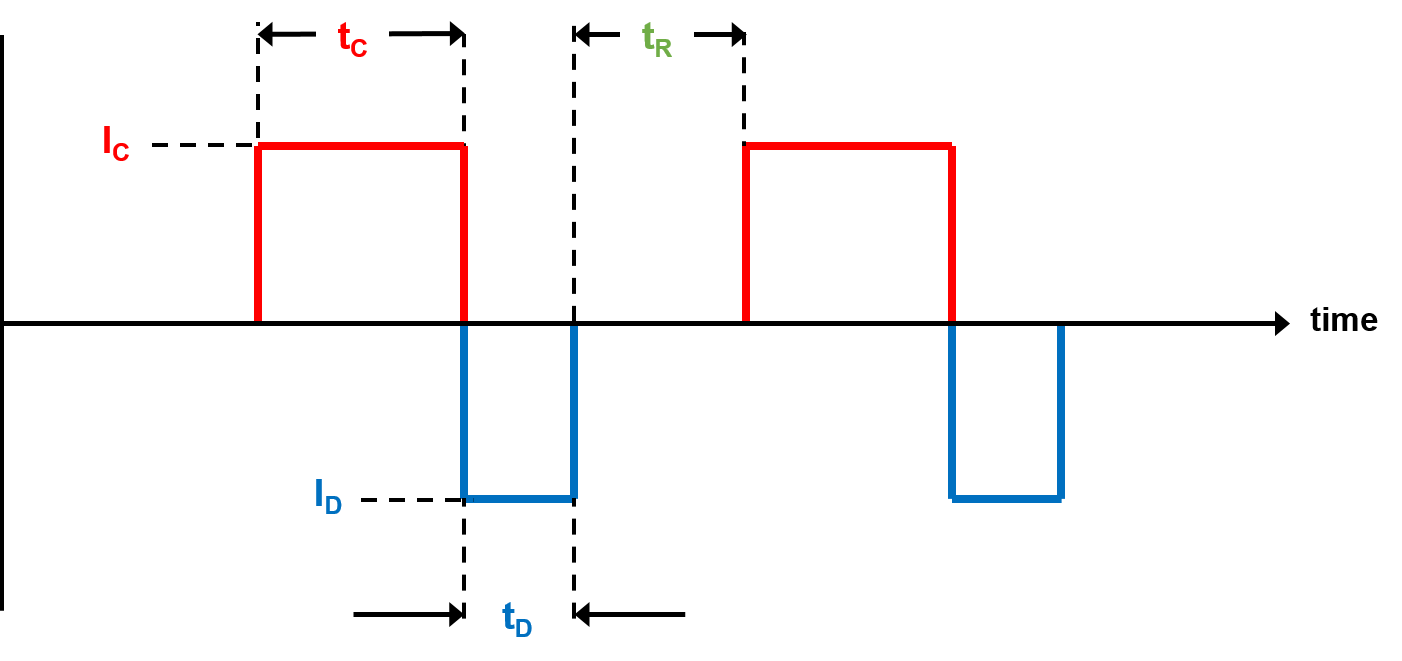
The following is a brief explanation of our charge algorithm. A simple graph below depicts the critical parameters.
 |
Our rapid charge technique is comprised of three fundamental components:
|
During the entire charging process, battery temperature, voltage and current are continually monitored and modulated by the proprietary Chargetek/PDI software and the parameters of the algorithm are adjusted in real time during the charge.
For example, the industry standard charging current is based upon the amp hour (Ahr) rating of the battery and is denoted by C. If a battery has a capacity of 500Ahr, then the standard charge rate would be in the range of C/3 - C/5 resulting in a charging current range of 100 - 170 amps. There would be variations depending upon the characteristics of a particular battery. For this particular application, the charge current would be set to 2C (1000A) with a 50% duty cycle resulting in a charge rate of C or 500 amps. The discharge current would subtract from this slightly. The resulting charge time would be approximately 1.1 hours. This charge time is two to three times faster than what would be attainable using a conventional charger. With a conventional charger, the charge current would be limited to a maximum of C/3 or 170 amps.
Click on the boxes below for more about our rapid charging technology
 |
 |
| Chargetek, Inc. 1860 Eastman Avenue Unit 109 Ventura, CA 93003 Phone: (805) 482-7930 Fax: (805) 482-7936 www.chargetek.com |
||||
| Home | Product overview | CK & CT 150 | Custom chargers | |
| About | Product selector guide | CT 500 | Rapid charging technology | |
| Sales inquiries | Battery charger basics | DPIC | Waterproof battery chargers | |
| Contact | Choosing a charger | RTIC-WP | Fan cooled battery chargers | |
| Sitemap | Charging system configurations | RTIC-FC | AC/DC battery chargers | |
| Glossary | TPRO | DC/DC battery chargers | ||
| FAQs | APLC | Lithium battery chargers | ||
| DPLC | ||||
| © 2015 Chargetek, Inc. | ||||